
Hypoxia Product Specialist for Don Whitley Scientific, Omar Hussain, shares some of his PhD research and how he used the Whitley H35 Hypoxystation in the phenotypic screening of hypoxia-activated prodrugs.
Inefficient vascular supply to solid tumours results in the generation of a tumour microenvironment (TME) that has a profound effect on tumour biology and response to therapy [1-3]. The TME is characterised by an oxygen gradient (hypoxia) and a low extracellular pH (pHe) (Figure 1) [2,3].
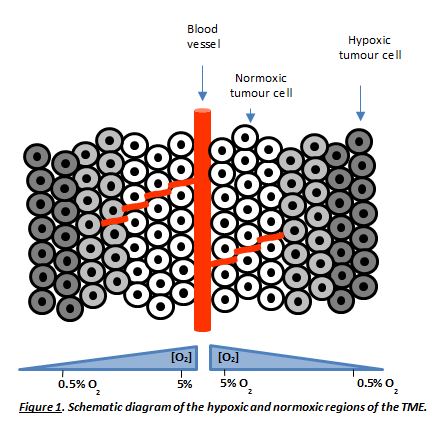
Cancer cells within hypoxic regions (low oxygen) are typically resistant to current chemotherapeutic drugs [4]. This indicates the need to develop new therapeutics that target cancer cells under such an environment [5]. Hypoxia has many biological and therapeutic implications which contribute to some hallmarks of cancer such as promoting angiogenesis [6] and increased invasion and metastasis [7]. Hypoxia activated prodrugs (HAPs) are compounds that become activated under low oxygen tension and mild acidic conditions, [5] which were paved by Alan Sartorelli in the 1970s. This offers a dynamic opportunity to target these tumour resistant cells. Despite 40 years of research there is still no HAP that is approved by the food and drug administration (FDA) for clinical use, which exemplifies the importance of the development of HAPs to target the hypoxic niche in the TME.
As part of my PhD studies (under the direct supervision of Professor Roger Phillips, University of Huddersfield) I investigated the cytotoxic and selective ability of a series of hypoxia activated prodrugs (HAPs) by way of phenotypic screening under normoxic and hypoxic conditions. Once the hit compounds were identified, I further investigated these compounds mechanistically under hypoxic conditions. All of the hypoxia work was carried out using a Whitley H35 Hypoxystation.
I carried out the following in the Whitley H35 Hypoxystation:
- Routine cell culture and maintenance of the following cell lines
- Colorectal cancer
- HCT116(P53 +/+), HCT116(P53 -/-), HCT116(KRAS Mutant) and HCT116(KRAS Wildtype)
- Pancreatic cancer
- Mia-PaCa-2
- Breast cancer
- MCF-7, MDA-MB-231
- I would normally have 1 or 2 T75 cm2 flasks of each cell line in the Hypoxystation at a time.
- Phenotypic screening
- Carried out by using the MTT assay (3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium)
I would place on average 20-30x 96 well plates in the Hypoxystation at a time.
- Western blot analysis
- For the detection of h2ax phosphorylation for early signs of DNA damage all cells were treated with hit compound and lysed inside the hypoxic chamber
- For the detection of SRC, phosphorylated SRC 527 and phosphorylated SRC 416 for the tyrosine kinase inhibitor dasatinib and the hit compound. Again cells were lysed in the hypoxic chamber
- Scratch assay
- To assess the ability of cell migration under normoxic and hypoxic conditions
All of this work was carried out using the following equipment inside the Whitley H35 Hypoxystation:
- Pipette gun, serological stripettes (5mL, 10mL and 25mL)
- Pipettes, P10, P20, P200, P1000, P5000 and an 8 channel multi-pipette
- Pipette tips
- 20µL tip box x1
- 300µL tip box x2
- 1000µL tip box x 2
- 5000µL tip box x1
- 1x 500mL waste beaker
- Dependent on experiment approx. 10-12 channel reservoirs at a time

The Hypoxystation was reserved using a booking system on a daily basis by various members within the institute to ensure fair usage. My personal experience with the Whitley H35 Hypoxystation was very positive as there were no issues throughout the duration of my PhD other than the basic wear and tear of the cuffs. As we had the gold service package, the Hypoxystation was serviced annually and there was an element of ease knowing that any issues could be rectified swiftly. Having used the H35 Hypoxystation extensively throughout my PhD, as well as gaining knowledge in cancer pharmacology and drug discovery, it was natural for me to pursue a career as a hypoxia product specialist for Don Whitley Scientific.
References
- Ahmadi, M., et al. (2014). Hypoxia modulates the activity of a series of clinically approved tyrosine kinase inhibitors. British Journal of Pharmacology 171(1): 224-236.
- Brown, J. M. (2002). Tumor microenvironment and the response to anticancer therapy. Cancer Biology & Therapy 1(5): 453-458.
- Vaupel, P. (2010). Metabolic microenvironment of tumor cells: a key factor in malignant progression. Exp Oncol 32(3): 125-127.
- Saggar, J. K., et al. (2013). The tumor microenvironment and strategies to improve drug distribution. Frontiers in oncology 3. 154.
- Phillips, R. M. (2016). Targeting the hypoxic fraction of tumors using hypoxia-activated prodrugs. Cancer chemotherapy and pharmacology 77(3): 441-457.
- Harris AL (2002) Hypoxia–a key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nat Rev Cancer 2:38–47
- Chang Q, Jurisica I, Do T, Hedley DW (2011) Hypoxia predicts aggressive growth and spontaneous metastasis formation from orthotopically grown primary xenografts of human pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res 71:3110–3120 7.


 CH
CH

 English
English